📢 转载信息
原文链接:https://machinelearningmastery.com/the-complete-guide-to-data-augmentation-for-machine-learning/
原文作者:Kanwal Mehreen
在本文中,您将学习使用数据增强来减少过拟合和提高图像、文本、音频和表格数据集泛化能力的实用、安全的方法。
我们将涵盖的主题包括:
- 增强的工作原理以及何时有帮助。
- 在线与离线增强策略。
- 图像(TensorFlow/Keras)、文本(NLTK)、音频(librosa)和表格数据(NumPy/Pandas)的实操示例,以及数据泄露的关键陷阱。
好了,我们开始吧。
机器学习数据增强的完整指南
图片作者提供
假设您已经构建了机器学习模型,运行了实验,并对结果感到困惑,不确定哪里出了问题。训练准确率看起来不错,甚至可能令人印象深刻,但当您检查验证准确率时……效果却不理想。您可以通过获取更多数据来解决这个问题。但这既耗时、昂贵,有时甚至是不可能的。
这并非是凭空捏造假数据。而是通过对已有的数据进行细微修改,同时不改变其含义或标签,来创建新的训练样本。您以多种形式向模型展示同一个概念。您是在教导模型什么重要,什么可以忽略。增强有助于模型泛化,而不是简单地记忆训练集。在本文中,您将了解数据增强在实践中如何工作以及何时使用它。具体来说,我们将涵盖:
- 什么是数据增强以及它如何帮助减少过拟合
- 离线数据增强与在线数据增强的区别
- 如何使用TensorFlow对图像数据应用增强
- 文本数据的简单安全增强技术
- 音频和表格数据集的常见增强方法
- 为什么增强过程中的数据泄露会悄无声息地破坏您的模型
离线与在线数据增强
增强可以在训练前或训练期间发生。离线增强仅扩展数据集一次并保存。在线增强则在每个周期(epoch)生成新的变体。深度学习管道通常偏爱在线增强,因为它能让模型接触到有效不受限制的变化,而无需增加存储空间。
图像数据增强
图像数据增强是最直观的入门点。一只狗即使经过轻微的旋转、缩放或在不同光照条件下观察,它仍然是狗。您的模型需要在训练期间看到这些变化。一些常见的图像增强技术包括:
- 旋转 (Rotation)
- 翻转 (Flipping)
- 调整大小 (Resizing)
- 裁剪 (Cropping)
- 缩放 (Zooming)
- 平移 (Shifting)
- 剪切 (Shearing)
- 亮度和对比度变化
这些变换不会改变标签——只改变外观。让我们使用TensorFlow和Keras来演示一个简单的例子:
1. 导入库
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
|
2. 加载 MNIST 数据集
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# Normalize pixel values
X_train = X_train / 255.0
X_test = X_test / 255.0
# Reshape to (samples, height, width, channels)
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
X_test = X_test.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)
# One-hot encode labels
y_train = to_categorical(y_train, 10)
y_test = to_categorical(y_test, 10)
|
输出:
|
1
|
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/mnist.npz
|
3. 定义用于增强的ImageDataGenerator
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=15, # rotate images by ±15 degrees
width_shift_range=0.1, # 10% horizontal shift
height_shift_range=0.1, # 10% vertical shift
zoom_range=0.1, # zoom in/out by 10%
shear_range=0.1, # apply shear transformation
horizontal_flip=False, # not needed for digits
fill_mode='nearest' # fill missing pixels after transformations
)
|
4. 构建一个简单的CNN模型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
model = Sequential([
Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
Flatten(),
Dropout(0.3),
Dense(64, activation='relu'),
Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
|
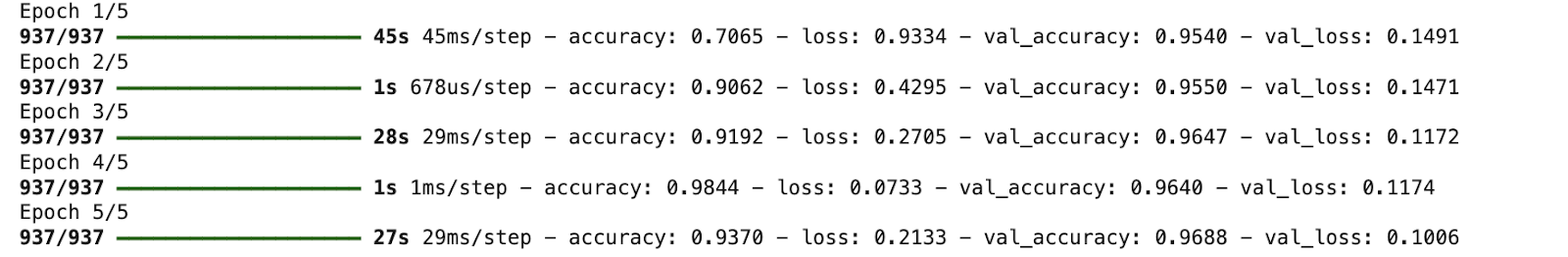
5. 训练模型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
batch_size = 64
epochs = 5
history = model.fit(
datagen.flow(X_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True),
steps_per_epoch=len(X_train)//batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_data=(X_test, y_test)
)
|
输出:
6. 可视化增强后的图像
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Visualize five augmented variants of the first training sample
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 2))
for i, batch in enumerate(datagen.flow(X_train[:1], batch_size=1)):
plt.subplot(1, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(batch[0].reshape(28, 28), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
if i == 4:
break
plt.show()
|
输出:

文本数据增强
文本更加微妙。您不能随意替换单词而不考虑其含义。但是,小的、受控的更改可以帮助模型泛化。这是一个使用同义词替换(结合NLTK)的简单示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import wordnet
import random
nltk.download("wordnet")
nltk.download("omw-1.4")
def synonym_replacement(sentence):
words = sentence.split()
if not words:
return sentence
idx = random.randint(0, len(words) - 1)
synsets = wordnet.synsets(words[idx])
if synsets and synsets[0].lemmas():
replacement = synsets[0].lemmas()[0].name().replace("_", " ")
words[idx] = replacement
return " ".join(words)
text = "The movie was really good"
print(synonym_replacement(text))
|
输出:
|
1
2
|
[nltk_data] Downloading package wordnet to /root/nltk_data...
The movie was truly good
|
含义相同。新的训练样本。在实践中,像nlpaug这样的库或反向翻译API常被用于获得更可靠的结果。
音频数据增强
音频数据也从增强中受益良多。一些常见的音频增强技术包括:
- 添加背景噪音
- 时间拉伸 (Time stretching)
- 音高偏移 (Pitch shifting)
- 音量缩放 (Volume scaling)
最简单和最常用的音频增强之一是添加背景噪音和时间拉伸。这有助于语音和声音模型在嘈杂的现实环境中表现得更好。让我们通过一个简单的例子(使用librosa)来理解:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
import librosa
import numpy as np
# Load built-in trumpet audio from librosa
audio_path = librosa.ex("trumpet")
audio, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=None)
# Add background noise
noise = np.random.randn(len(audio))
audio_noisy = audio + 0.005 * noise
# Time stretching
audio_stretched = librosa.effects.time_stretch(audio, rate=1.1)
print("Sample rate:", sr)
print("Original length:", len(audio))
print("Noisy length:", len(audio_noisy))
print("Stretched length:", len(audio_stretched))
|
输出:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Downloading file 'sorohanro_-_solo-trumpet-06.ogg' from 'https://librosa.org/data/audio/sorohanro_-_solo-trumpet-06.ogg' to '/root/.cache/librosa'.
Sample rate: 22050
Original length: 117601... [内容被截断]
|
🚀 想要体验更好更全面的AI调用?
欢迎使用青云聚合API,约为官网价格的十分之一,支持300+全球最新模型,以及全球各种生图生视频模型,无需翻墙高速稳定,文档丰富,小白也可以简单操作。


评论区